Highlights
 Beijing
Beijing
Highlights
Great Wall
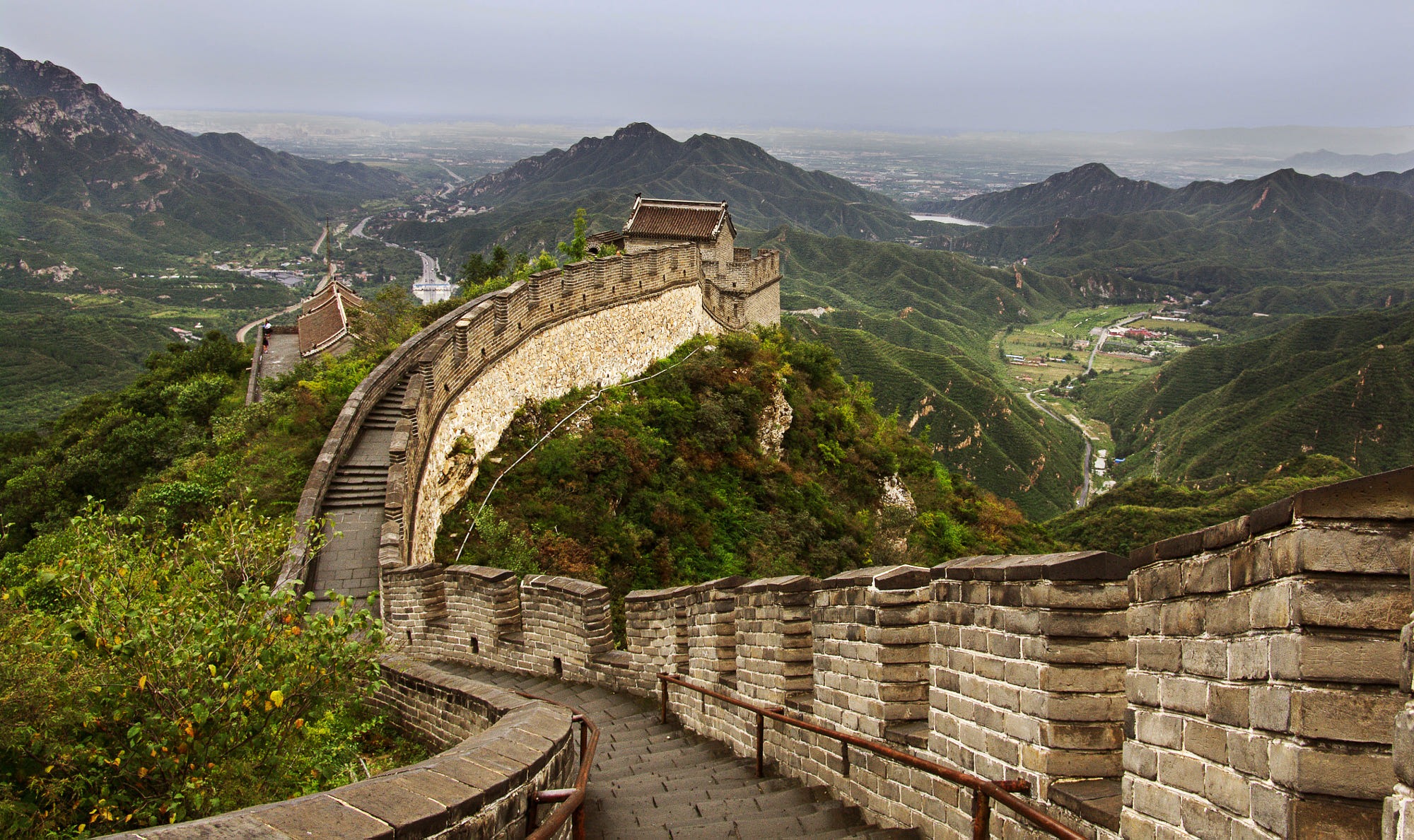
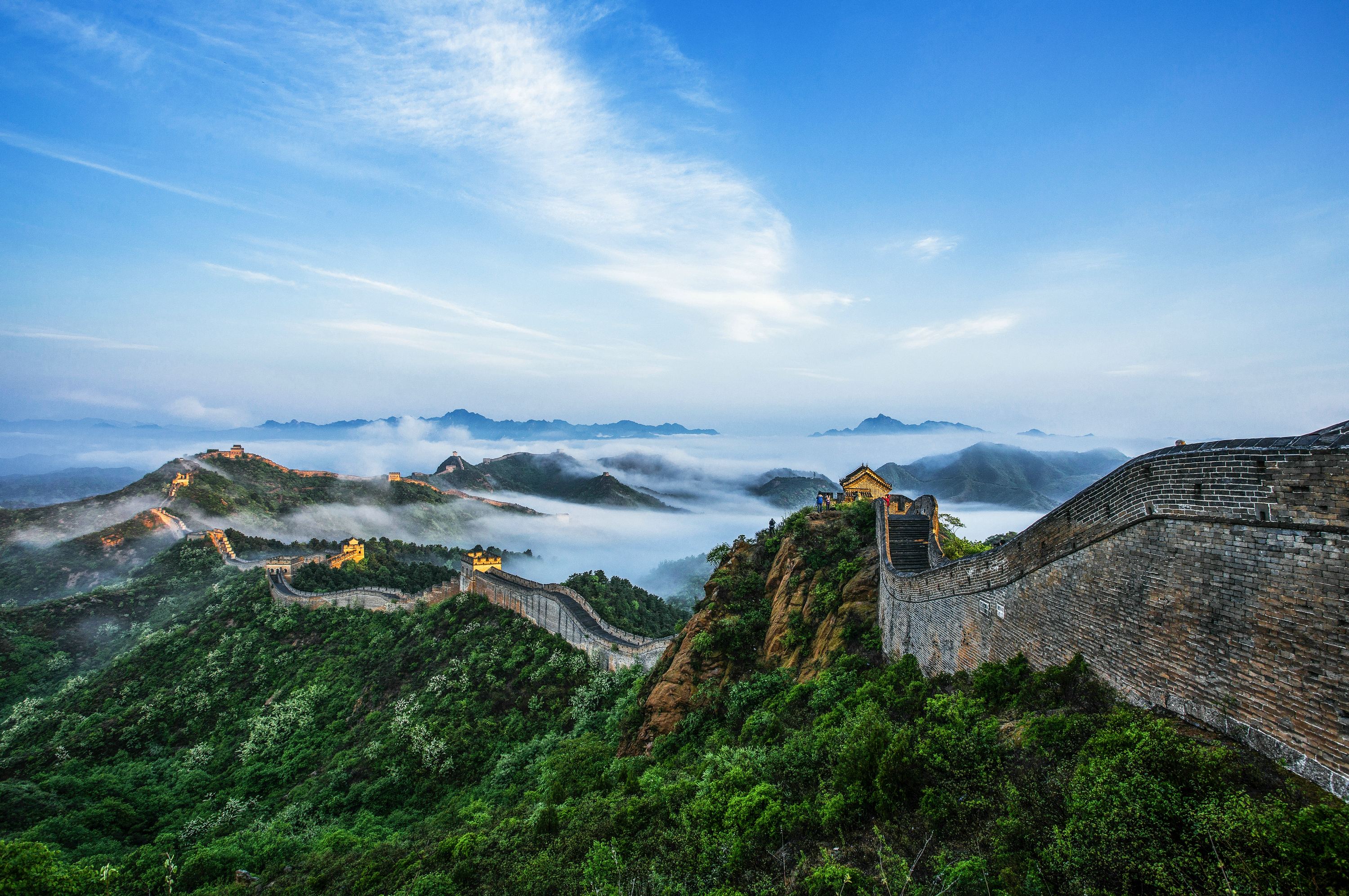


It is without doubt that the Great Wall is the greatest of civil engineering project of defense in ancient China. With its gigantic scale and difficulties in its construction, it is regarded as one of the great wonders in the history of mankind. The Great Wall is really the glory of the Chinese nation, which symbolizes the ancient culture and the long-standing history of China. Stretching over the mountain ranges, it proudly shows its magnificence to us. So to speak, the Great Wall has witnessed the rises and falls of innumerable dynasties and changes on the earth. At present, though the Great Wall is no longer served as a work of military defense against harassment and invasion. It still plays an important role in linking the Chinese people with the people of the rest of the world. It is one of the great bridges that build up friendship between different peoples.
The Great Wall is starting from the Old Dragon Head of the Shanhai Pass at the seaside in the east to a distance of 10,000 li (1 kilometer= 2 lis) in the west. Snaking along the north of China, it crosses three provinces, two municipalities and two autonomous regions. It is about 6,300 kilometers long, an equivalent of about 3,915 miles.
The present-day Great Wall originated from the early ancient Chinese history. During the time of Warring States Period (475-221 B.C.), in the purpose of defending themselves and against the infringement from the neighboring states, all the principal states had the walls built in the bordering areas of the territories. For example, the three states of Qin, Zhao and Yan had high walls and fortresses built along their northern frontiers to ward off the harassment by the Huns (an ancient nomadic tribe in China) from the north. In 221 B.C., the whole China was unified by the first emperor of the Qin Dynasty to defeat the six other ducal states. The emperor gave order to link up all the walls built by the former ducal states along the northern frontiers to prevent disturbing and attacking by the Huns. And these walls form the world famous “10,000-li Great Wall”. From generation to generation, the succeeding dynasties kept on the work of maintenance and repairs or having parts reconstructed time and again. Among them, the greatest project on scale in the old days of China was carried out in the Han and Ming dynasties.
Throughout history, the Great Wall is served as the traditional defensive project. It is mainly composed by passes, walls, watchtowers and beacon towers. Builders were forced to rely upon local materials for the wall inched across the Chinese wilderness. For example, some wall was built with tamped-earth, some with stone, some with tamped mixture of reed, red willow, and sands, and some with bricks outside and stuffed earth and sands inside. The walls we see today are mainly Ming walls, primary made of stone and bricks. The key parts of the military construction are Watchtowers. They are very close to each other, among which brick towers could be two or three storeys. There is a small room on the top of the tower, surrounded by battlements. The watchtower was also used to station soldiers or store food and weapons. Thousands of passes stretch along the Great Wall. Some are between the mountains, some between the mountains and rivers, and some between the mountains and sea. During the wars, passes are the strongholds by acting as the gateways of transportation. Beacon towers are used for communicating, which can deliver the emergent military messages in a very short time.
Just like the symbol of China—dragon, the Great Wall snakes from east to west on the Oriental. Nowadays, five sections of the Great Wall are opened to public in Beijing, including Badaling section, Juyong Pass section, Mutianyu section, Jinshanling section and Simatai section.
Badaling Section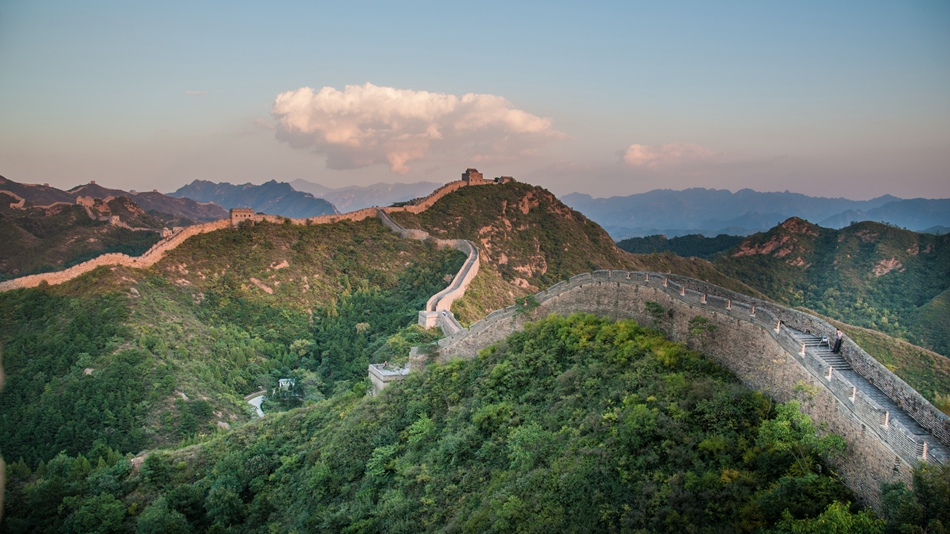
Badaling section is the outstanding part of the Great Wall. Lying in the Yanqing District, sixty kilometers northwest of Beijing, it gives vital protection for the Juyong Pass, which is one of the key passes of the Great Wall. According to its strategic importance of commanding, Badaling section is known as "giving access to every direction", which gains it the name Badaling.
Badaling was built in an early time in the ancient Chinese history. During Spring and Autumn Period and Warring States Period, defensive wall was constructed along the Yanshan Range to resist the marauding of the nomadic tribes. Since then the following dynasties continued to fortify the Badaling section. The wall we see today was constructed in Ming Dynasty (1368-1644 A.D.) along the ridges of mountains. The construction lasted about a hundred years long from 1505, the 18th year of Emperor Hongzhi, to the reign of Emperor Wanli.
The huge Badaling wall was strongly and firmly built. It was based on the foundation of granite slabs, surrounded by a facing of kiln-fired bricks, and covered with bricks on the top. All stuffed with pulverized lime, the slots could enable the wall to be smooth. The height of the wall is 8.5 meters. It is 6.5 meters wide at the bottom and 5.7 meters wide on the top, making it possible for 5 horses or 10 people march abreast on the top. Watchtowers are 0.5 or 1 kilometer apart from each other, which were full of vigor and grandeur, and orderly spotted the wall. The battlements and embrasures of the watchtower were in good condition in wartime. The wall winds its way along the ridge of the Jundu Mountain, rising abruptly to the peaks of each side of the Badaling. You will be amazed by its seemingly endlessness. It stretches far away into the remoteness. The wall of Badaling is 3, 741 meters long.
Among all the parts of the whole Great Wall, Badaling was the earliest section to be open to the tourists. Badaling has received 130 million tourists home and abroad. Among them, there are 370 foreign leaders and very important persons who have come to climb Badaling successively.
Mutianyu Section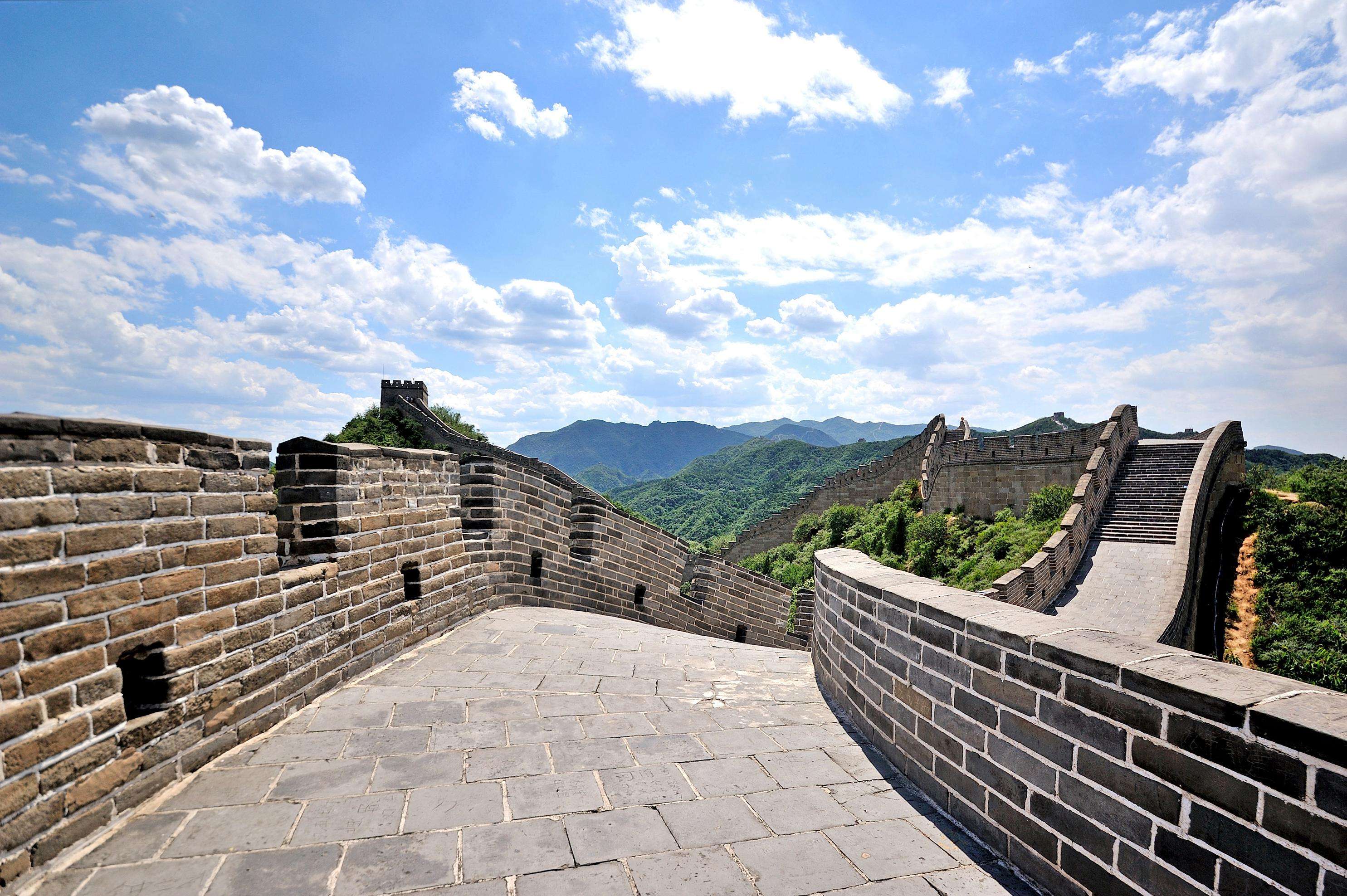
Mutianyu section is 75 kilometers northeast of Beijing. Lies in Huairou District, it links Juyong Pass in the west with Gubeikou Pass in the east. Mutianyu section is called as the Majestic Pass on Precipitous Mountains, commanding its strategic importance.
Because of its relatively gentle terrain, watchtowers of Mutianyu section were built in large numbers to strengthen its defensive functions. The closest watchtowers are less than 50 meters apart from each other. Both arms of the Mutianyu section stretch upwards along the ridges of continuous mountains. On the foundation of the Ming Dynasty wall The Mutianyu section was mainly built on precipitous mountains and 5-7 meters high. It is featured with a thick cluster of watchtowers atop, strategic passed, majestic vigor and unique structure. In this section, the gate tower is the most unique building.
Simatai Section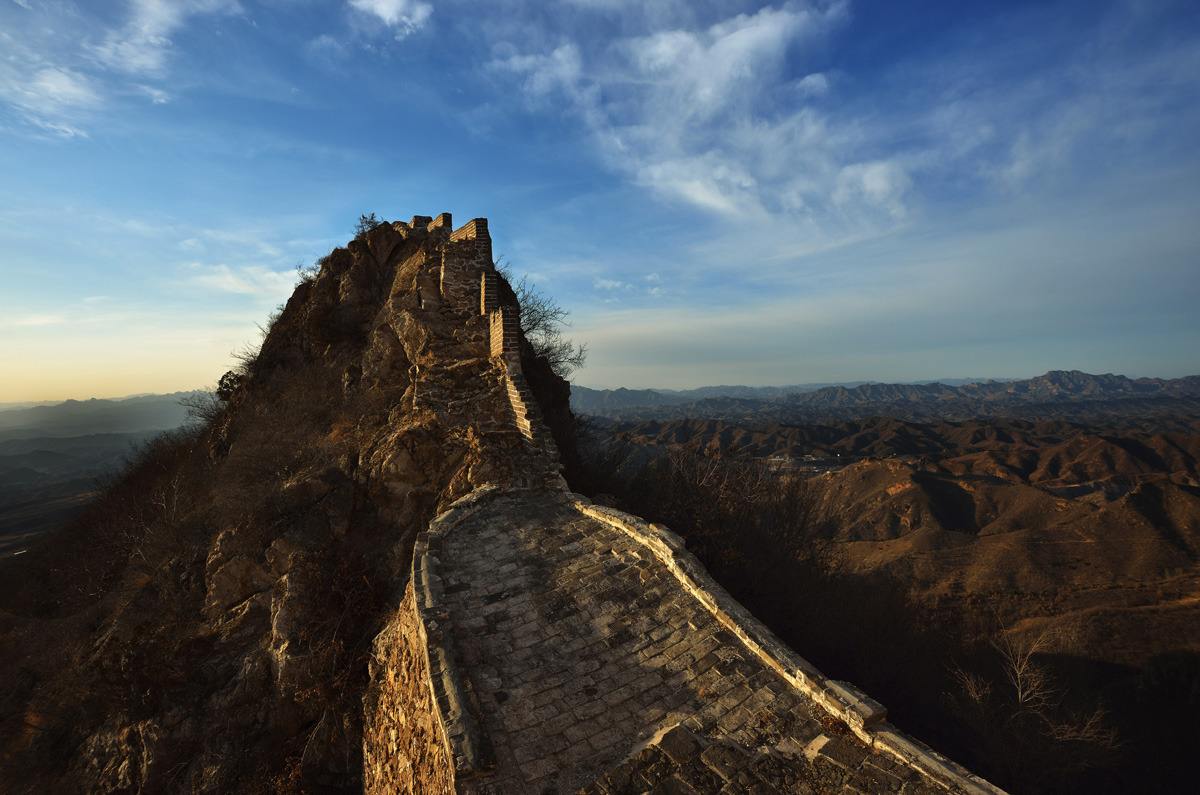
Simatai Section lies in the Miyun County, 120 kilometers away from Beijing. It started from Wangjing Tower in the east and connected with Jinshanling section in the west. Without hordes of other tourists, it is a largely unrestored and more authentic section of the Great Wall.
Simatai section was constructed during the early years of Ming Emperor Hongwu. It is said that there was a renovation applying from 1569 to 1573. It was mainly built along the ridge of the mountains because of its location in the mountainous area. Featuring in uniqueness, ruggedness and trimness, it perfectly coordinates with the undulating terrain, which makes it more majestic and magnificent. Simatai reservoir is situated at the foot of the central part of the Simatai section, which is 600-700 meters long with the storage capacity of 50,000 cubic meters.
Simatai section is considered to be the most wonderful part of the Great Wall. Taking good advantage of the fluctuating terrain, the walls and watchtowers constitute the most essential part of the wall. It is famous for its precipitous cliffs, magnificent towers, suspension walls and rugged stairways. If you are looking from distance, you may find that the Great Wall is just like a flying dragon in the cloud. However, when you stand nearby, the wall stretches its arms along the ridges of mountains. All these make it the most amazing part of the Great Wall.
Jinshanling Section
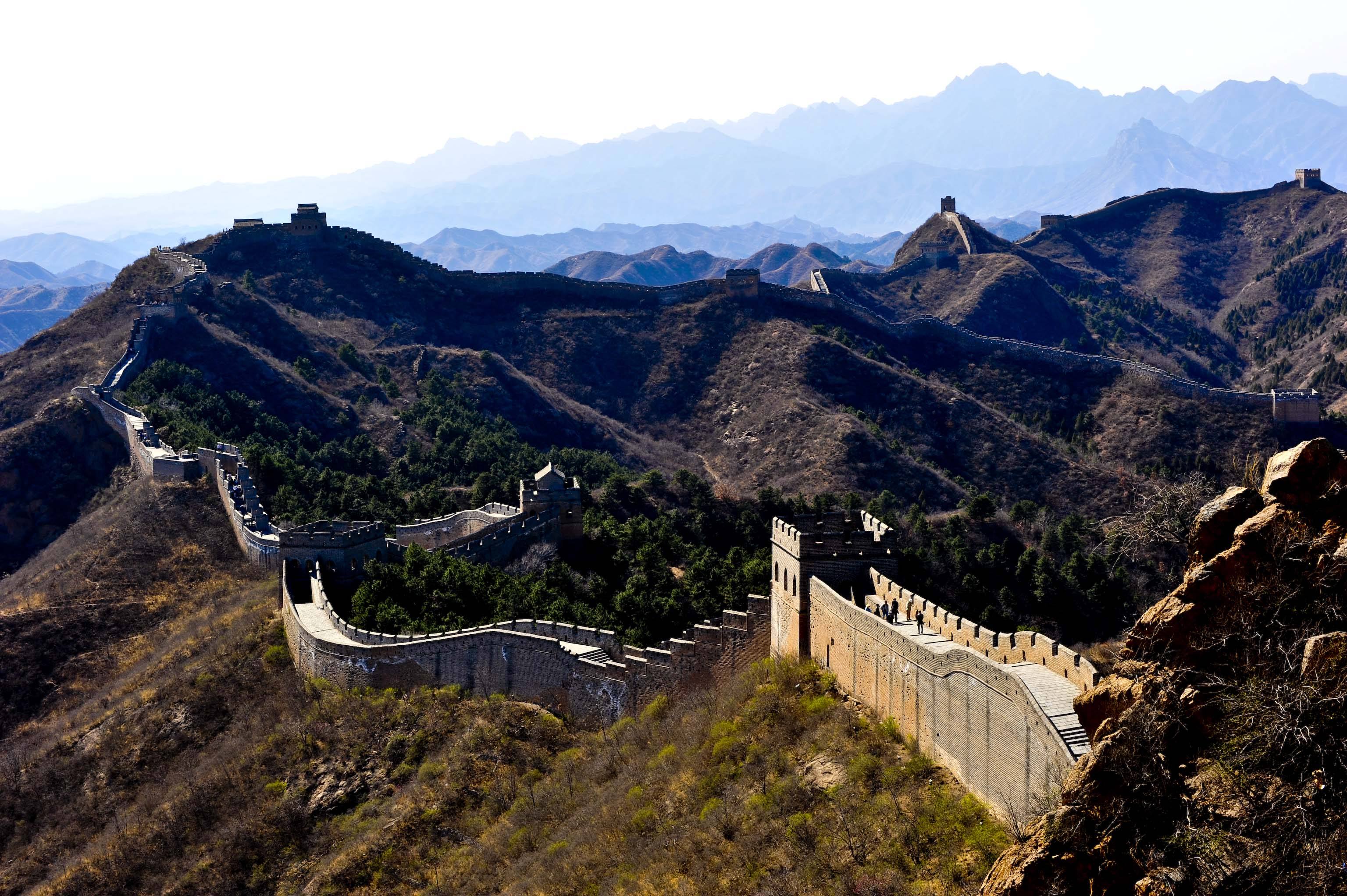

The Jinshanling Great Wall was initially built from 1368 to 1389 in the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644), and in 1567 and 1570 rebuilding of the Wall was mainly directed by General Qi Jiguang (1528-1588). Poems and tablet writings can be found on the Jinshanling Great Wall left from the time when Qi Jiguang directed the rebuilding of this section of the Great Wall. Continue to read more on the Great Wall history. Jinshanling is connected to the Simatai Great Wall in the east and the Panlongshan Great Wall in the west. Jinshanling has probably the highest frequency of towers per kilometer of any place along the Ming Dynasty Great Wall. It also has one of the greatest varieties of architectural and defensive styles of both wall and towers.
The total length of this section is about 11 kilometers (6.8 miles). The Wall is about 7 meters high and 5 meters wide, and is made of brick and stone. The Jinshanling Great Wall has an elevation of 700 meters. There are more than 100 watch towers along the Jinshanling Great Wall. ‘Watching Beijing Tower’ is on the highest point, from which you can see Beijing. The Jinshanling Great Wall is second only to the Badaling Great Wall in its completeness.
Tian’anmen Square
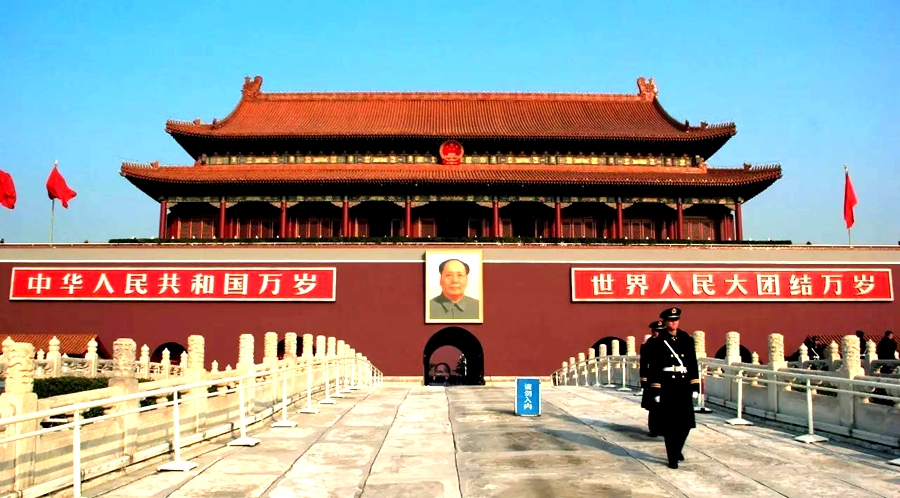

Tian’anmen(Gate of Heavenly Peace), situated at the center of Beijing meaning in English, symbolizes the People's Republic of China. Built in 1417, it was formally called Chengtianmen (Gate of Heavenly Succession). At that time, it was the front gate of the Imperial City. By the end of the Ming Dynasty, the uprising farmers led by Li Zicheng entered the city, but later when the Qing army marched upon Beijing, the Chengtianmen was destroyed under the crossfire. In 1651, it was rebuilt and named "Tian'anmen".
The Tian'anmen Rostrum, as a place to hold ceremonies of great importance, such as promulgating an imperial edict conferring the title of a queen, or announcing a newly enthroned emperor, was made known to the public all over the country. During the Ming and Qing dynasties, it was popular to hold the Imperial Exam system for choosing high-ranking officials by way of a palace examination, which supervised by the emperor himself. If the examinees ranked the first three, they would be entitled. What’s more, they would have the honor to be granted an audience by the emperor two days after the examination. On that day they would be called in to see the emperor in turn in the Tian'anmen Rostrum.
There is a square running 880 meters from south to north and 500 meters from east to west in front of the Tian'anmen Rostrum. It is the Tian'anmen Square – the very center of Beijing. Tian'anmen Square is the largest city square in the world with an area of 44 hectares.
During the Ming and Qing dynasties, the Tian'anmen Square was a piece of land in front of the Imperial Palace, an open space jetting out towards the south from the Tian'anmen Gate. It had a meaning of embodying the outstanding importance of the Tian'anmen Gate and the Imperial City. In the early days of the Ming Dynasty, a gate of brick and stone was built, which is right on the site of the present Memorial Hall of Chairman Mao Zedong, called Damingmen (Gate of the Great Ming). In the Qing Dynasty it was renamed as Daqingmen (Gate of Great Qing) and after 1911 Zhonghuamen (Gate of China). Later on, another two gates of brick and stone structure were built on each site of the avenue in front the gate. Surrounded by a newly built red wall, the area within the three gates formed a small square of only 11 hectares-- Tian'anmen Square.
During the Ming and Qing dynasties, common people were forbidden to enter the Tian'anmen Square. And for the officials, when they entered the gate, they had to get off horses and proceed on foot into the palace. The government offices were lined outside the wall on the east and west. According to the traditional system, the civil service organizations were set in the eastern part of the square, and the military organizations in the west.
Old buildings in the Tian'anmen Square were put down after the collapse of the Qing Dynasty in 1911. In 1957, the square expanded with an area of 44 hectares, which may hold 1 million people at a time. With Chairman Mao's Memorial Hall right behind, the Monument to the People's Heroes towered in the center of the square. To the east of the Square, there is the National Museum of China and to the west the Great Hall of People (National People's Congress building).
The Monument to the People's Heroes is the largest monument in China's history which was built in 1952. On this monument, you can see the words--"The People's Heroes are Immortal", which were written by Chairman Mao. The development of Chinese modern history and those who contributed their lives to the democratic progress are shown by the eight unusually large relief sculptures. The monument is enclosed by two rows of white marble railings. It seems very simple and beautiful.
At the south side of the Square is the Memorial Hall of Chairman Mao Zedong. This Hall is consisted by three halls, among which our dear Chairman Mao's body lies in a crystal coffin in the halls surrounded by fresh bouquets of various famous flowers and grasses.
The Great Hall of the People is in the west of the Square. Constructed in 1959, this building is the site of the China National People's Congress meetings, which also provides an impressive site for other political and diplomatic activities. With twelve marble posts, the Hall includes three parts--the Central Hall, the Great Auditorium and a Banqueting Hall. The ceiling of the Central Hall is decorated with crystal lamps and the floor paved with marble. The Great Auditorium behind the Central Hall can hold 10,000 people, while the huge Banqueting Hall can seat 5,000.
At the east side of the Square stands the China National Museum, which is another important place for you to visit. Built in 2003, it is a mergence of China History Museum and China Revolutionary Museum. This National Museum is on the opposite of the Great Hall of the People. In the China Revolutionary Museum, there are a lot of material objects, pictures, books and models, presenting the development of modern China. A large number of cultural relics are exhibited in the China History Museum, illustrating the long history and glorious culture of China from 1,700,000 years ago to 1925 when the last emperor left the throne.
Forbidden City
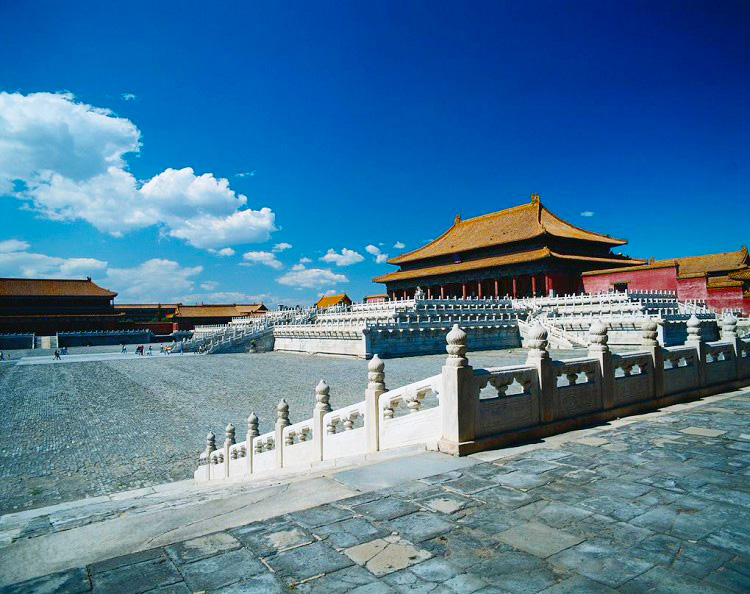

The Palace Museum, the imperial palace in the Ming and Qing dynasties, is the largest and best-preserved palace complex in the world today. It is also called the Purple Forbidden City in Chinese. Its name, on one side, derives from ancient Chinese astronomers' belief that God's abode or the Purple Palace. The pivot of the celestial world, is situated in the Pole Star (the middle of the Ziwei Star), at the center of the heaven. Therefore, the son of God of Heaven--the emperor, should live in the Purple City. On the other side, without special orders of the emperor eunuchs and guards, ordinary citizens were not allowed entering the Forbidden City, except for palace maids. For this reason, palaces in the Ming and Qing dynasties are called both the Forbidden City and the Purple City.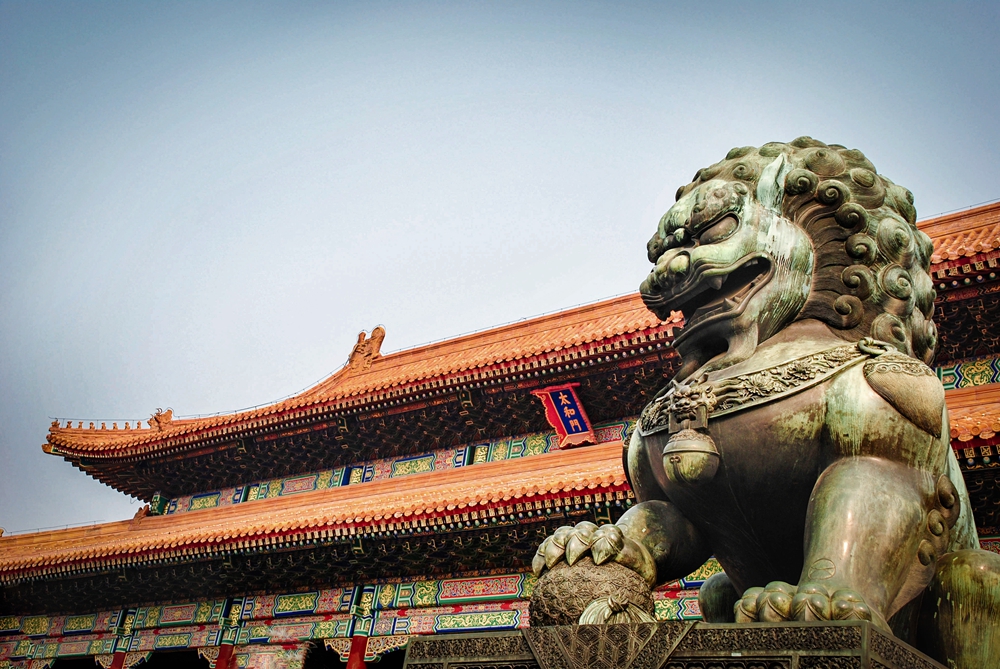 The Construction of the magnificent palace started in 1406, and ended in 1420. It took 14 years to complete the project. One year after completion, Emperor Yongle moved his capital from Nanjing to Beijing. Since then, 24 emperors have lived at the Forbidden City, 14 during the Ming Dynasty and 10 during the Qing Dynasty.
The Construction of the magnificent palace started in 1406, and ended in 1420. It took 14 years to complete the project. One year after completion, Emperor Yongle moved his capital from Nanjing to Beijing. Since then, 24 emperors have lived at the Forbidden City, 14 during the Ming Dynasty and 10 during the Qing Dynasty.
The Forbidden City covers an area of over 720,000 square meters, 750 meters wide and 960 meters long. And it has four great gates. The fabulous city, which is surrounded by a 52-meter-wide moat, has four delicate and lovely turrets overlooking both the inside and outside.
The Forbidden City has more than 8,700 wooden rooms, most of which have yellow-glazed tiles. It is a color that only emperors were allowed to use on their roof. From the northern Drum Tower and the Bell Tower to the Southern Gate of Everlasting Stability (Yongdingmen), these colorfully painted and embellished rooms are divided symmetrically into northern and southern halves. If you walk into the city, you will see the layers of halls and palaces spreading out on either side of a central axis. As the designations of the wise architectures, the splendid buildings represent the unique features of the traditional Chinese architecture and embody the incredible creativity of the ancient Chinese people. Reconstructed after being destroyed by several fires, this pearl of Chinese cultural heritage still retains its original arrangements of the Ming dynasty. Nowadays, most of the existing buildings open to visitors were reconstructed during the early Qing Dynasty.
In many ways the Forbidden City reveals ancient Confucian ideas, as it is generally designed to the principles of the Front court, Rear Market, Ancestral Sacrifice on the left and Altar on the right. Hence, the court was located in the southern or front section of the Forbidden City, where officials discussed political affairs. A large trading market was situated in the rear part of the city, providing daily necessities for the court. On the left side was the Imperial Ancestral Temple, where the emperor offered sacrifices to his ancestors. Nowadays, it is the Working People's Cultural Palace. On the right side was the Altar to the god of Land and Grain, where the emperor displayed his reverence to the god. This is now Zhongshan Park.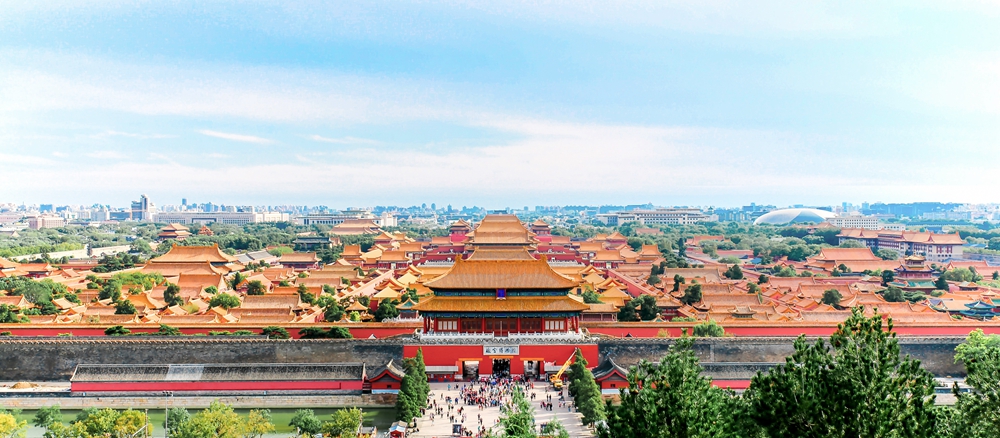
There are two courts in the Forbidden City: the Inner Court and the Outer Court. They are separated across the middle between the south and north ends. The Outer court is mainly composed by the Meridian Gate and the Three Front Halls, flanked by the Hall of Literary Glory (Wenhuadian) and the Hall of Martial Spirit (Wuyingdian), which witnessed various ceremonies and political activities during the Ming and Qing dynasties. While the inner court is mainly consisted by the Three Back Halls, Imperial Garden, Hall of Mental Cultivation and Palace of Abstinence, which are flanked by the Six East Halls and the Six West Halls. This was the place where the emperor was confronted with political affairs and was the residential area for the emperor and his empresses and concubines.
Compared with other contemporary palaces, the Forbidden City stressed more on balance and independence, and embodied more cultural perspectives of the specific ethnic group. Just as what was written in the book of History of Chinese Science by Joseph Needham, each part of the Forbidden City is in well balance and independence, which is just on the contrary to other palaces in the Renaissance Age. For the city, the Palace of Versailles is just acting as an object. The palace is an organic part of the whole city, combining deep deference to nature with lofty significance. As a tin far-reaching and complicated Chinese architecture, Great overall arrangements have reached the highest level, far above any other culture.
After the subversion of the Qing Dynasty by the Revolution of 1911, the last emperor Pu Yi was exiled to palaces at the rear of the Forbidden City. In 1914, the Three Great Halls in the Imperial Palace was opened as exhibition hall of antiquities. Ten years later, Feng Yuxiang staged a coup in Beijing and expelled the last emperor from the palace. Oct. 10, 1925 established The Palace Museum. And in 1961, the Forbidden City was listed as a place to be given special protection by the State Council. UNESCO listed it as World Cultural Heritage site in 1987.
The Forbidden City, as one of the world-famous royal palaces, has played an important role in the world architectural history. Many tourists both from home and abroad have been attracted by the almost 1 million rare treasures and cultural relics on exhibition there.
Summer Palace
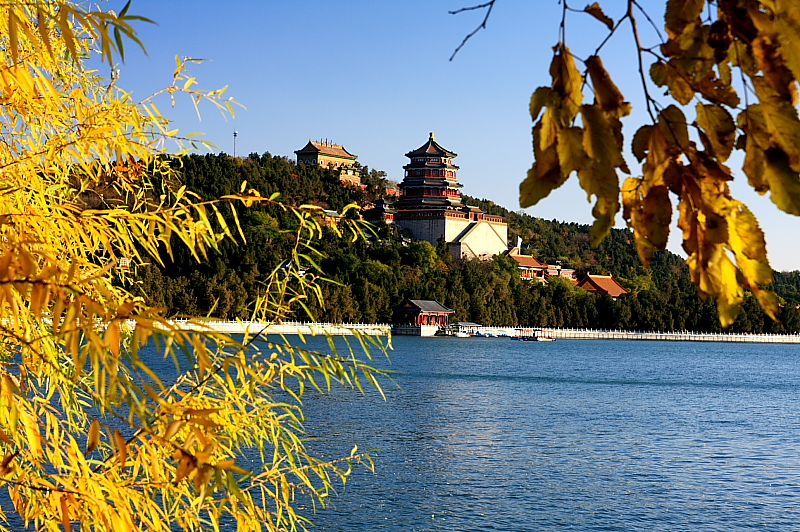

Covering an area of 290 hectares in total, the Summer Palace spreads out some 15 kilometers away from the city center in the north western suburbs of Beijing. Three fourths of the palace is covered by a pool of water and the rest the land and hills.
The Summer Palace is the summer resort of the Qing royal family. Now it is the most intact, the best-preserved and the largest of its kind of the classical gardens in the country. Since the garden began to be built in 1153, it had undergone many a time reconstruction and renovation in the Yuan and Ming dynasties. In the period of Emperor Qianlong’s reign of the Qing Dynasty, it was still reconstructed in a large-scale. And this time was renamed the "Garden of Crystal Ripples". When it was completed in 1860, it suffered a severe destruction, led by the Anglo-French Allied Army, which brought it down to ashes. In 1886, Empress Dowager Cixi embezzled the funds allocated for the building of the navy to rebuild it and renamed it the "Summer Palace". However, in 1900, it underwent destruction again by the Eight Powers Allied Forces. Later, the1903 saw its second-time rebuild.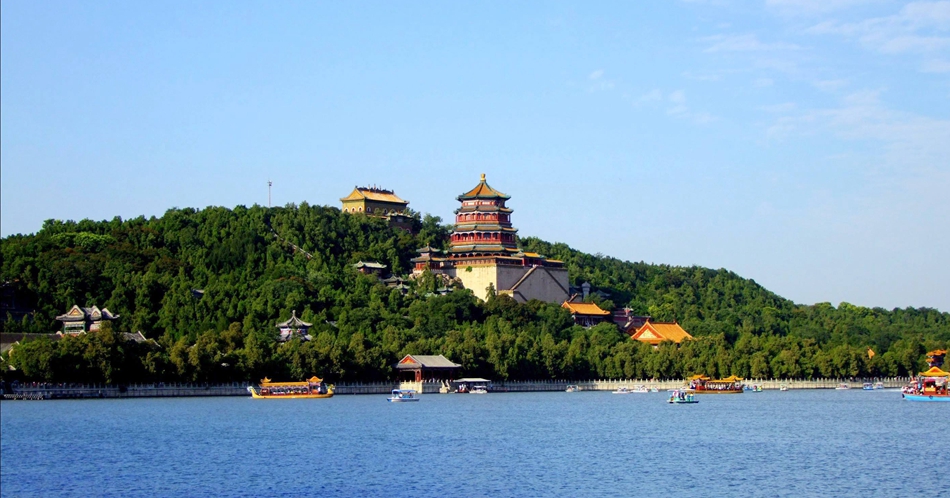
On the 12th of October 1911, Empress Dowager Longyu was finally forced to promulgate the abdication of the royal power. However, according to the agreement between the Qing royal family and the republic government, the Summer Palace would still be kept in the hands of the Qing royal family, while yet to be opened to outside as private property by selling admission tickets. 1924 when Puyi was ousted, the Summer Palace was taken over by the republic government and changed to be a public park.
The Qing royal family stayed in the Forbidden City in spring, autumn and winter. And when it came to summer, they went to their summer resort –Summer Palace. Hence, the Summer Palace shares the same functional quarters as that in the Forbidden City. Among these quarters, the office quarter, the living quarter and the entertainment quarter formed the magnificent scenery in Summer Palace.
Through the East Palace Gate, there is the Hall of the Benevolence and Longevity. The emperor used to handle state affairs and listen to reports by ministers and receive foreign envoys in there. It was called the Hallo of Diligent Administration by Emperor Qianlong during his reign. In 1860, it was burnt down by the Anglo-French Army. Reconstructed In 1890, it was then renamed the "Hall of the Benevolence and Longevity". During the reigns of Emperors Tongzhi and Guangxu, Empress Dowager Cixi got the real power to rule the country, and she started to handle state affairs behind the screen.
The Hall of Jade Ripples and the Hall of Happiness and Longevity are the three parts of the living quarter. Guangxu used to live in the Hall of Jade Ripples Emperor in the Summer Palace. After his failure of the Reform Movement of 1898, Emperor Guangxu was put into house arrest here. Thus, it is also regarded as an exquisitely decorated jail.
Consisting of four rooms, the Hall of Happiness and Longevity used to be the residence for Empress Dowager Cixi. The Empress moves to the Summer Palace and stays there in the hall every year on the first day of the fourth month in the lunar calendar. And she won't return until the tenth of the tenth lunar month when she had celebrated her birthday there. In the Summer Palace, there are over 1,000 people dancing attendance on the Dowager. Among them, there are 48 in the Hall of Happiness and Longevity, of whom 20 are maids-in-waiting, 20 eunuchs of importance and another 8 are the "ladies-in-waiting" by her side, normally waiting in the room behind the precious throne to attend on her.
The Long Corridor, the starting point of entertainment quarter, is at the end of the courtyard of the Hall of Happiness and Longevity. It is 728 meters long with more than 14,000 traditional Chinese paintings on the beams and rafters. The four pavilions along the corridor represent the four seasons a year. The Marble Boat can be found at the end of the Long Corridor. The original Chinese style of it was burnt down by the Anglo-French Army in 1860. In 1893, it was rebuilt into one of a western style, imitating a steam ship with two water-wheelers. In 1903 Empress Dowager Cixi built another storey of wooden structure with the decoration of colored pieces of glass. The construction of this immovable boat was to symbolize the stable and consolidated rule of the Qing regime just like a large piece of rock. It would stand still forever in the vast ocean and would, under no circumstances whatsoever be wavered or toppled.
Occupying three fourths of the total area of the Summer Palace, Kunming Lake plays important role in the adjustment of the temperature in the garden. Taking a walk in the Long Corridor and a dragon boat on the lake, you will have a wonderful feeling that you were the emperor and empress in ancient China.
Temple of Heaven
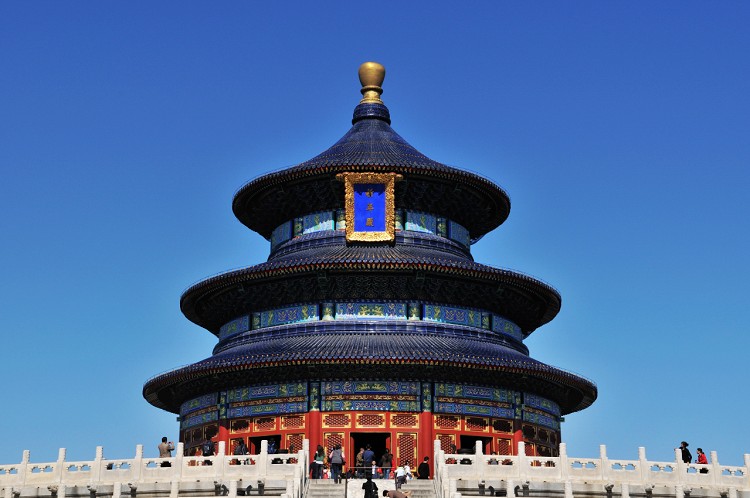

The Temple of Heaven stands in the southern part of Beijing. It was used to be the house ceremonies of emperors of worshipping heaven and praying for harvest in the Ming and Qing dynasties. This altar temple remains to be the largest existing ancient sacrificial structures across the world, more important than other three major temples, i.e. Altar to the Earth, Altar to the Sun and Altar to the Moon.
The Temple of Heaven was built in 1407 and the construction of the project took 14 years. Covering an area of 273 hectares, with two surrounding rings walls, it is four times bigger than the Forbidden City. The wall, stretching from north to south, is as long as 1,657 meters and that from east to west 1,703 meters. The outer wall is 6,553 meters in circumference while the inner wall measures 4,152 meters in perimeter.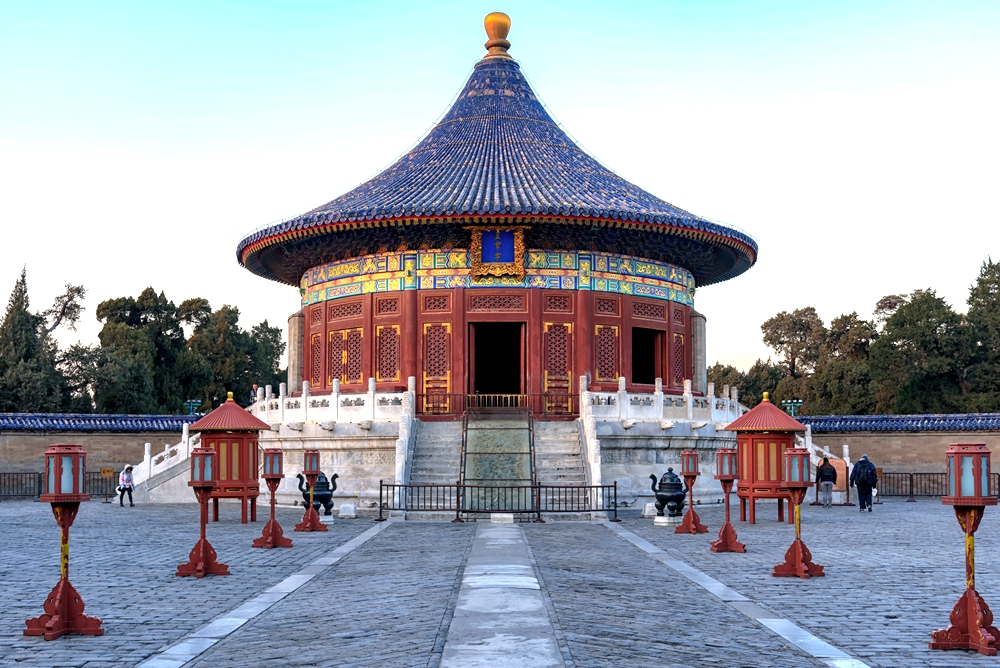
To pray for good harvests and fine rain, emperors did regular worshipping and offered sacrifices to heaven. And the Temple of Heaven was used to the place where emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties went and worshipped the heaven twice (and sometimes three times) a year. In the past, the tradition went that sacrifices were offered to heaven and earth in one place only. But in 1530 when the Temple of Earth was built in the north of the city, the Temple of Heaven was ever since used specially for offering sacrifices to heaven alone.
The Temple of Heaven is consisted by three sections, named the Circular Mound Altar, the Imperial Vault of Heaven and the Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests, attached with some affiliated buildings like Dressing Platform, Long Corridor and Echo Wall.
The Circular Mound Altar was first constructed in 1530. In ancient China, to some extend, the altar was a place that even more important than the Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests. The emperor would come to offer sacrifices to heaven on the altar every year on the day of the Winter Solstice. For this reason, the altar was rebuilt into a circular one in 1749. Built in the open air without shelter, the sacrificial ceremony was being held right under heaven. Therefore, it was called "Luji", or the "open air offering of sacrifices".
The Imperial Vault of Heaven was first built in 1530 as a main building in the south of the Temple of Heaven. At first, it was called "Taishendian" or the Hall for Pacifying Gods, but later changed into the present name. In 1752, the building was rebuilt into one of a single eave, which used to have double eaves. Standing 19.5 meters high and of 15.6 meters in diameter, the circular hall used to be an octagonal one in the past. The tablet of the Jade Emperor, the four stone platforms on both sides used to be for the tablets of the emperor’s ancestors of eight generations in succession, is consecrated on the central stone-platform in the Hall of Imperial Vault of Heaven.
Being of 32.72 meters in diameter, built on a three-tired platform, the Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests towers 38 meters' high with its eaves fanning out on three tiers, of which the upper one has a gold-plated knob on it. You will be amazed to see that such a heavy building was supported only by 28 wooden pillars with no single piece of reinforced concrete at all. The whole building was built by mortise and tenon joints without using a single nail. With each pillar in height of 19.2 meters, the four pillars in the center of the hall are called "Longjingzhu"--the Dragon Well Pillar. Only by joining hands together by two and half persons, can it be embraced. These four pillars indicate the four seasons of a year. You may find it more interesting that all pillars have their special meanings: the outside 12 pillars suggest 12 months in a year and another 12 pillars in the round wall symbolize the 12 two-hour periods of a day. And when you put the two 12 pillars together, the number you get is 24, which represents the 24 solar terms of a year. And when you add the four in the center of the hall to 24, you will get 28, which represents the 28 lunar mansions in the heaven above.
Since its first construction in 1420, the Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests has gone through several times of changes. At that moment, the hall was called "Dasidian"--the Hall of Grand Sacrifices, which was rectangular in shape. But in 1529, it was reconstructed into a round one with a roof of three tiers. And this time it was named "Daxiangdian"--the Hall of Grand Treatment to Heaven. Three different colors were painted in these roofs of three tiers. From the upper tier to the lower one, the colors are respectively blue, yellow and green. In 1752, these three colors were all changed into glazed tiles of dark blue. However, they were destroyed by lightning in 1889. And later in 1890, it was restored according to the original. In 2006, the whole building was renovated with all its paintings according to the same style as they done last time. The Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests has become the symbol of Beijing.
At present, the Temple of Heaven is very popular with tourist home and abroad. It is also an entertainment center for local people. If you go to the temple early in the morning, you will find many local people practicing Taiji, playing cards and Chinese chess and singing folk songs there.
Ming Tombs
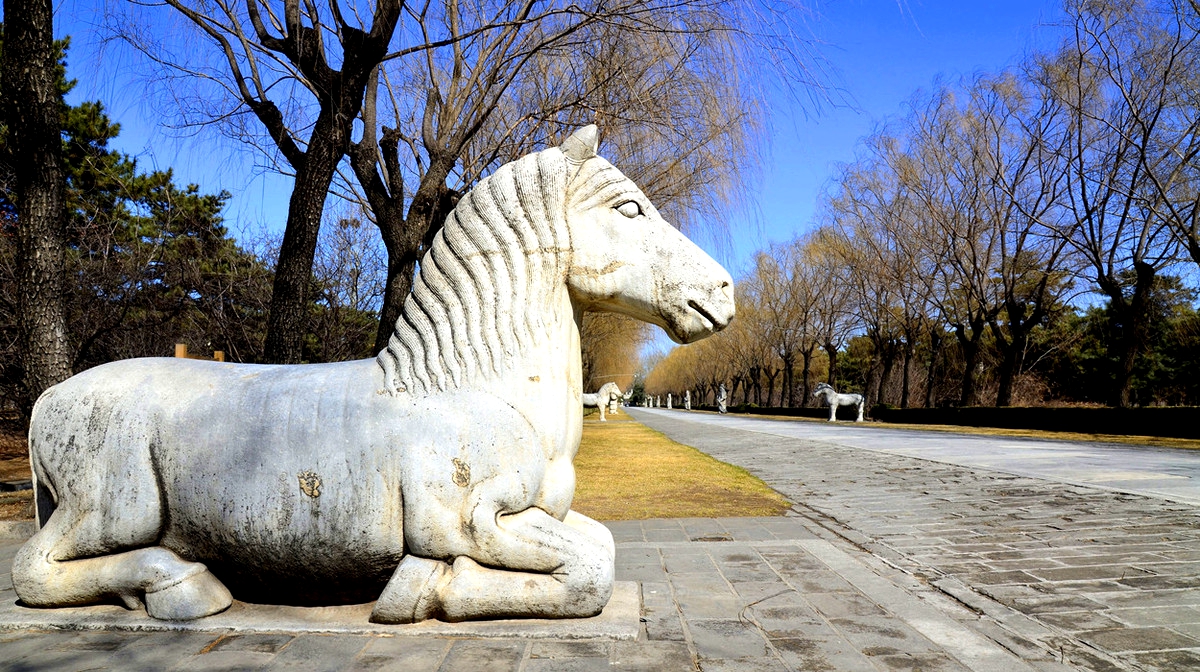

Covering an area of 40 square kilometers with 13 Ming emperors buried, the Ming Tombs is situated at the southern foot of the Tianshou Mountain in Changping District in the north western suburban areas of Beijing. The construction of the imperial tombs had been going on ceaselessly from the year 1409 when Emperor Zhu Di started building his tomb to the fall of the Ming Dynasty in 1644, lasting a period over 200 years.

As many people know, there are 16 emperors in the Ming Dynasty. Among the 16 Ming emperors, 13 of them were buried in this tomb area, except for Zhu Yuanzhang, the founder of the Ming Dynasty who was buried in the Xiaoling Mausoleum in Nanjing, Zhu Yunwen, who disappeared and Zhu Qiyu, who was buried at Jinshan Hill in the western suburbs of Beijing, all other. Therefore, this area was called the 13 Ming Tombs.
It was originally built only for Emperor Zhu Di and his empress, named Changling, which is the most magnificent tomb. The succeeding twelve emperors had their tombs built around Changling. At present, the two tombs opened to the public are Changling and Dingling.
Changling is the first Ming tomb built in this area. Hence, the axle line of Changling naturally became the axle line of the whole Ming Tombs. Along with the various tombs, the Stone Tablet House come together overall as a structurally and visually unified architectural accomplishment. Though these tombs were built in different periods, they were strategically planed and built in different stages. Each tomb has its own distinct adornments. However, the entire tomb area has a unified layout and style.
Zhu Di was the third emperor in the Ming Dynasty, who was buried together with his empress in Changling. During his 22-year of reign, he was, relatively speaking, an emperor who had made quite some achievements. For example, he determined to move the capital from Nanjing to Beijing in 1421. To some extend, the move itself was an expression of far-sightedness, for it was very important to strengthen the national defense and guard frontier areas. During the period from 1405 to 1424, Zheng He, also called Eunuch Sanbao, was sent by the emperor to fulfill a diplomatic mission which was on an ever larger and broader scale in Chinese history. He went six times on board across the sea to over 30 countries in Asia and Africa.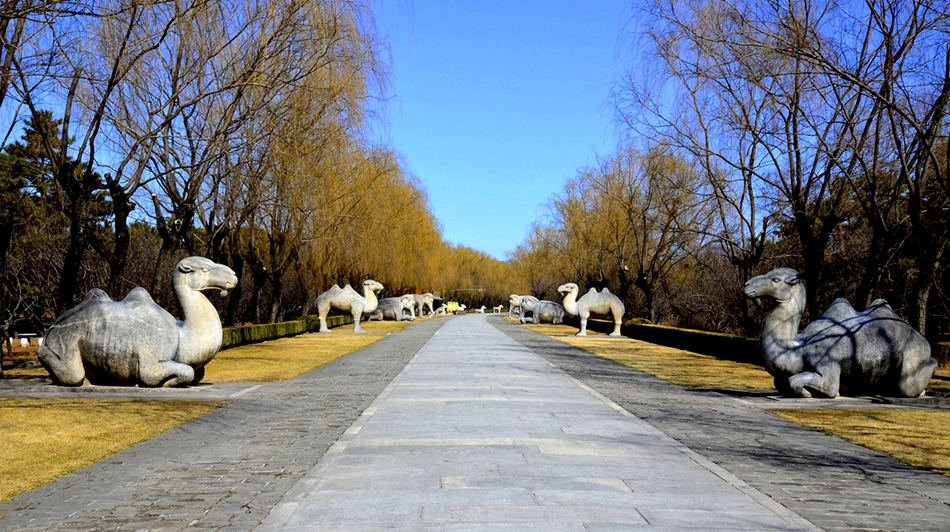
Completed in 1416, as the place for worshipping tablets of the emperor and empress and offering sacrifices to ancestors, the Hall of Eminent Favor is situated within the second compound of Changling. The Hall of Eminent Favor in Changling is the best-preserved among the ones of the 13 tombs, which duplicated the Hall of Supreme Harmony in the Forbidden City. It is a very precious relic of ancient China's wooden structures.
Dingling is the tomb for Emperor Zhu Yijun, named the tomb of Stability. It is said that he was buried together with his two empresses—Xiaoduan and Xiaojing. Ascending the throne at the age of 10, Zhu Yijun was died at 58 with a reign span of 48 years. Therefore he became the emperor with the longest time in power for in the Ming Dynasty. The construction of the Dingling tomb started in 1584. It took 6 years to bring the project to finish in 1590, covering an area of 180,000 square meters and costing 8 million taels of silver.
The Dingling began to be excavated in May 1956, which brought to light the mystery of the underground palaces of the Ming Tombs. Constructed with hard stone-slabs, with a total floor space of 1,195 square meters, the underground palace is composed by five beamless vaults, called the front, the middle, the rear and the two annexes on the right and the left. Carved out of white marble and the rear hall with the bier holding three coffins for the emperor and his two queens, three thrones were laid out in the middle vault. There are over 3,000 pieces of archeological findings unearthed from the tomb.
Yonghegong Lamasery
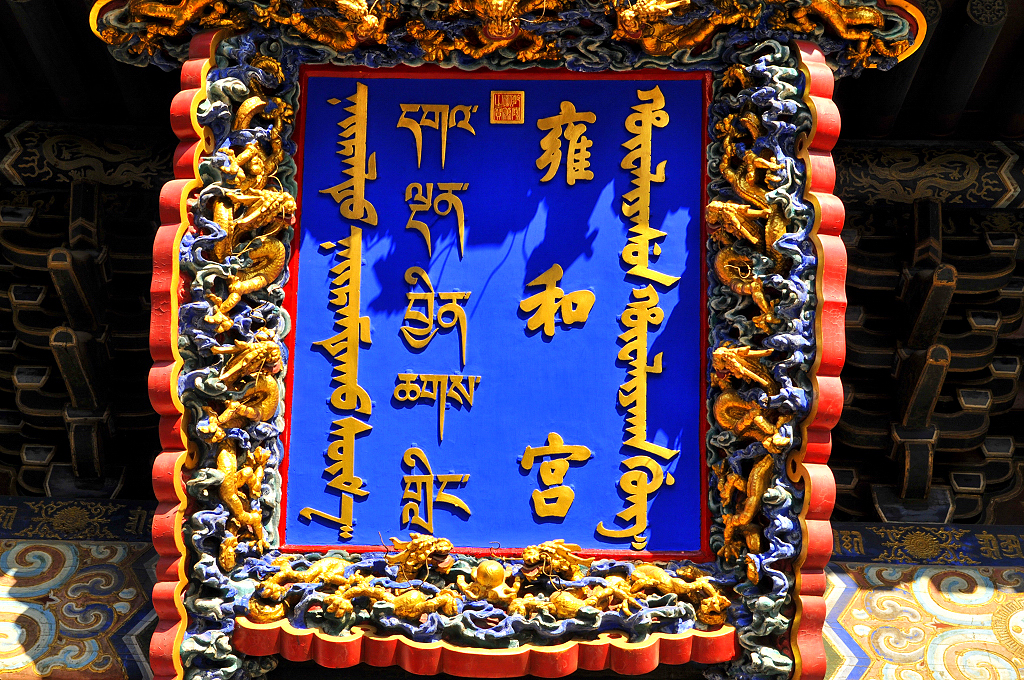

Yonghegong Lamasery is a well-known lama temple of the Yellow Hat Sect of Lamaism, which is located at the northeast part of Beijing. It was originally built in 1694 as the residence of Emperor Yongzheng of Qing (1644-1911 A.D.) before his ascent of the throne. And after his death, it was renamed Yonghegong. His successor Emperor Qianlong then rebuilt Yonghegong into an imperial palace with its turquoise tiles replaced by yellow tiles (yellow was the imperial color in the Qing Dynasty). In 1744, it became a lamasery. From then on, large numbers of monks from Mongolia and Tibet and national center of lama administration live in there.
As an imperial palace, the layout of the temple differentiated from other temples. The main gate faces to the south. There are five main halls and annex connected by courtyards on its 480-meter-long north-south axis, including a glaze-tiled arch, Gate of Peace (Zhaotaimen), Buddha's Warrior Hall (Tianwangdian), which was formerly the entrance to Yongzheng's imperial palace, Hall of Harmony and Peace (Yonghegong), Hall of Everlasting Protection (Yongyoudian), Hall of the Wheel of the Law (Falundian) and Pavilion of Eternal Happiness (Wanfuge).
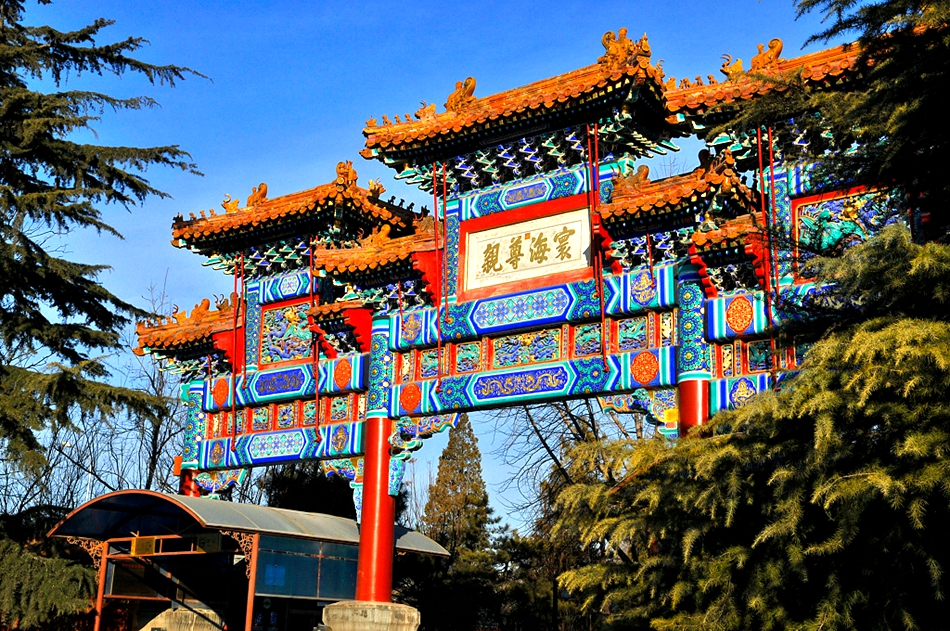

When you are walking through the grand glaze-tile arch patterned with decorative dragons and flowers in the first court, you will reach a three-arch gate - the Gate of Peace. In ancient times, the central passageway was for emperors. On each side of the second court next to the Gate of Peace stand the Bell Tower and the Drum Tower. Two pavilions stand symmetrically on opposite to the north. If you want to know more about the temple's history, you can have a look at the inscriptions of Chinese, Manchu, Mongolian and Tibetan engraved on steles.
The Buddha's Warrior Hall, also known as the Hall of Heavenly Kings, is the former entrance to Yongzheng's imperial palace. The hall Maitreya (Happy Buddha) was always used to greet visitors, which has a smiling face with a sandalwood pagoda on each side. Many small Buddhist images, symbolizing longevity, stand on the pagoda. Therefore, the pagoda is the Longevity Pagoda. There are four fearsome-looking Heavenly Kings or Celestial Guardians on both sides of Maitreya's shrine.
On the way to the Hall of Harmony and Peace stands a marble-based bronze incense-burner. With decorations of two dragons playing with a pearl on its six opens, it is 4.2 meters in height. Afterwards there is the Mount Sumeru, a bronze sculpture of Ming (1368-1644A.D.), representing the center of the world. On the top of it there lies a legendary paradise where Sakyamuni and men of moral integrity live after death; in the middle the dwellings of humans and below devils abide in hell.
The Hall of Harmony and Peace is formerly a place for the emperor Yongzheng to hold meetings. It was also called Mahavira Hall or Daxiongbaodian in Buddhism. Mahavira here is an honorable title of Sakyamuni in Chinese. Sakyamuni is on the altar, with Buddha of the Present in the middle with Buddha of the Past Yeja and the Buddha of the Future Maitreya on each side. On each side of the hall stand Statues of 18 Arhats. It is said that 18 Arhats were the disciples of Samkyamuni to diffuse Buddhism. The painting that you can find on the western wall is a Bodhisattva.
The Hall of Everlasting Protection (Yongyoudian) and the Hall of the Wheel of the Law (Falundian) are right behind the Hall of the Harmony and Peace, where enshrines a bronze image of Tsong Kapa -- founder of the Yellow Hat Sect. With 5 gold-plating pagodas, the golden-roofed Falundian was the place where lamas assemble to have religious activities. There is a 6-meter-high gilded bronze statue of Tsong Kapa on a lotus seat in the center of the hall.
Now there are nearly 70 lamas living in this temple. If you go there, you will find that regular religious activities are still practiced. More lamas can be seen coming here in the festival for lamas or Lamaism.
Old Beijing Hutongs

The numerous old hutongs are the distinguished features of Beijing. They symbolize the traditional community with small lanes, alleys and Siheyuan (quadrangle). The life of local people in these old hutongs makes this ancient capital look more charming. Wandering along these small lanes, you can see many quadrangles, called Siheyuan in Chinese, which are the residential quarters of natives. No one knows the exact number of these hutongs there are in Beijing.
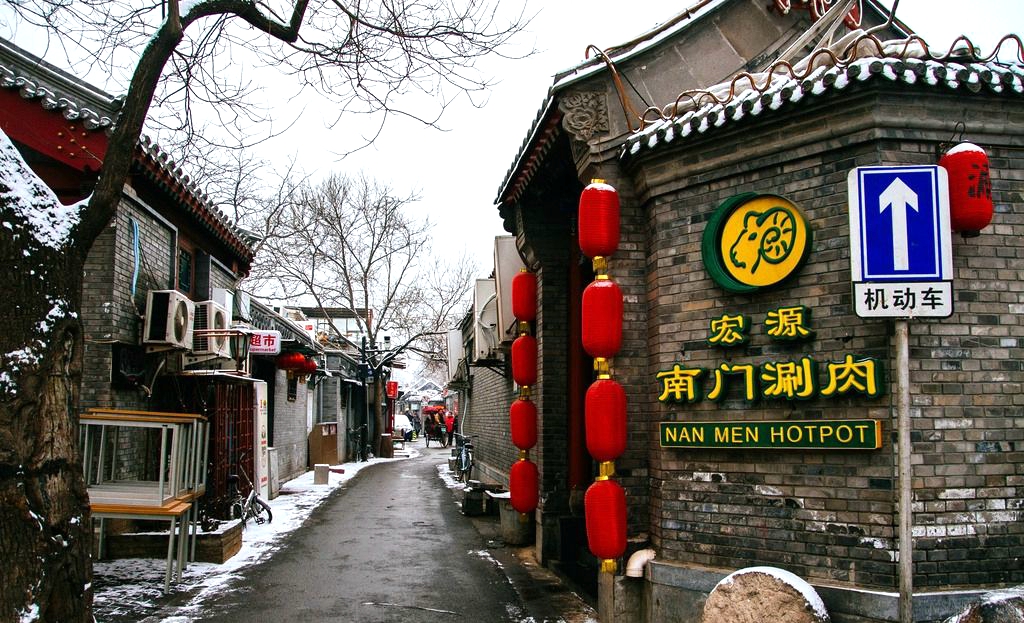

This tour shows you the modern and glamorous old Beijing .
Itinerary
After breakfast you will be picked up at your hotel, and we will take you to visit the [Nanluogu Xiang] (South Gong and Drum Lane, Nanluogu Alley) which is among one of the oldest hutongs around and has a history of over 800 years. This 800-meter long North-South alleyway is filled with bars, cafes, restaurants, artsy little shops, souvenir shops and cute boutiques. It's worth to spend an hour or two walking through the little alley ways and hutongs around it. Then you will visit [Shichahai] Shichahai is a famous scenic area that includes three lakes, surrounding places of historic interest and scenic beauty, and remnants of old-style Beijing residences, Hutong and Courtyard. This evening we will drive you to [Sanlitun Bar Street], Beijing's most well known bar street. And it is very popular with tourists and expatriates.
After all the visits, drive you back to the hotel. The tour ends when you are back to your hotel.
Meals included: Lunch
Pricing & Accommodation
-
 US Dollar
US Dollar -
 Euro
Euro -
 GB Pound
GB Pound -
 CA Dollar
CA Dollar -
 AU Dollar
AU Dollar -
 HK Dollars
HK Dollars -
 Renminbi
Renminbi
| Group Size | 1 person | 2-5 persons | 6-9 persons | ≥10 persons |
| Price(USD per person) | $225 | $140 | $80 | $50 |
* Price is in US dollar. It may vary a little bit according to US dollar exchange rate fluctuation, car fuel price change and government tax adjustment, etc.
* The price is only for your reference and it is subject to seasons, high or low.Please send us your inquiry if you are interested.
Inclusions / Exclusions
Inclusions:
A. Entrance fees for the attractions in the square brackets
B. Personal English-speaking Guide to be with you all the way
C. Experienced Driver + comfortable Private car/van/bus
D. Lunch
Exclusions:
A. Gratuities, Tips to the guide and driver
(Although not compulsory, if you think your guide and driver have done a good job at the end of the tour, we suggest you tip them at you own decision to show your appreciations.)
B. Other Personal Expenses.
Important Information
How to Dress (only for reference):
Comfortable walking shoes
Long, loose and comfortable pants
Shorts for summer months (June – September)
Shirts/T-shirts
Warm clothes (Fleece, Jacket, hat and gloves etc.) for Nov-April
Umbrella or waterproof jacket in a cloudy day or rainy day
Cover for backpack or plastic bags to keep clothes dry in case of rain
What to Bring (only for reference):
Wet wipes / Moist towelettes
Sun hat, Sun block, Sunglasses
Insect Repellent
Bottled Water
Small towel
Per Person
















